해당 프로젝트에서 GPT-2 모델을 구현하면서, 핵심 컴포턴트인, attention layer, postion embedding을 직접 구현
이후 HuggingFace에서 제공하는 pretrained weight를 로드해서 downstream task에 적용
you will build GPT-2, the precursor of OpenAI’s ChatGPT language model. Specifically, you will implement some of the most important components of the architecture, load the official model weights from HuggingFace into your implementation, and explore its capabilities on a variety of downstream applications
Model Architecture
class GPT2Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
# Embedding layers.
self.word_embedding = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, padding_idx=config.pad_token_id)
self.pos_embedding = nn.Embedding(config.max_position_embeddings, config.hidden_size)
self.embed_dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
# Register position_ids (1, len position emb) to buffer because it is a constant.
position_ids = torch.arange(config.max_position_embeddings).unsqueeze(0)
self.register_buffer('position_ids', position_ids)
# GPT-2 layers.
self.gpt_layers = nn.ModuleList([GPT2Layer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
# [CLS] token transformations.
self.pooler_dense = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size)
self.pooler_af = nn.Tanh()
# Final layer norm.
self.final_layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)Embedding Layer
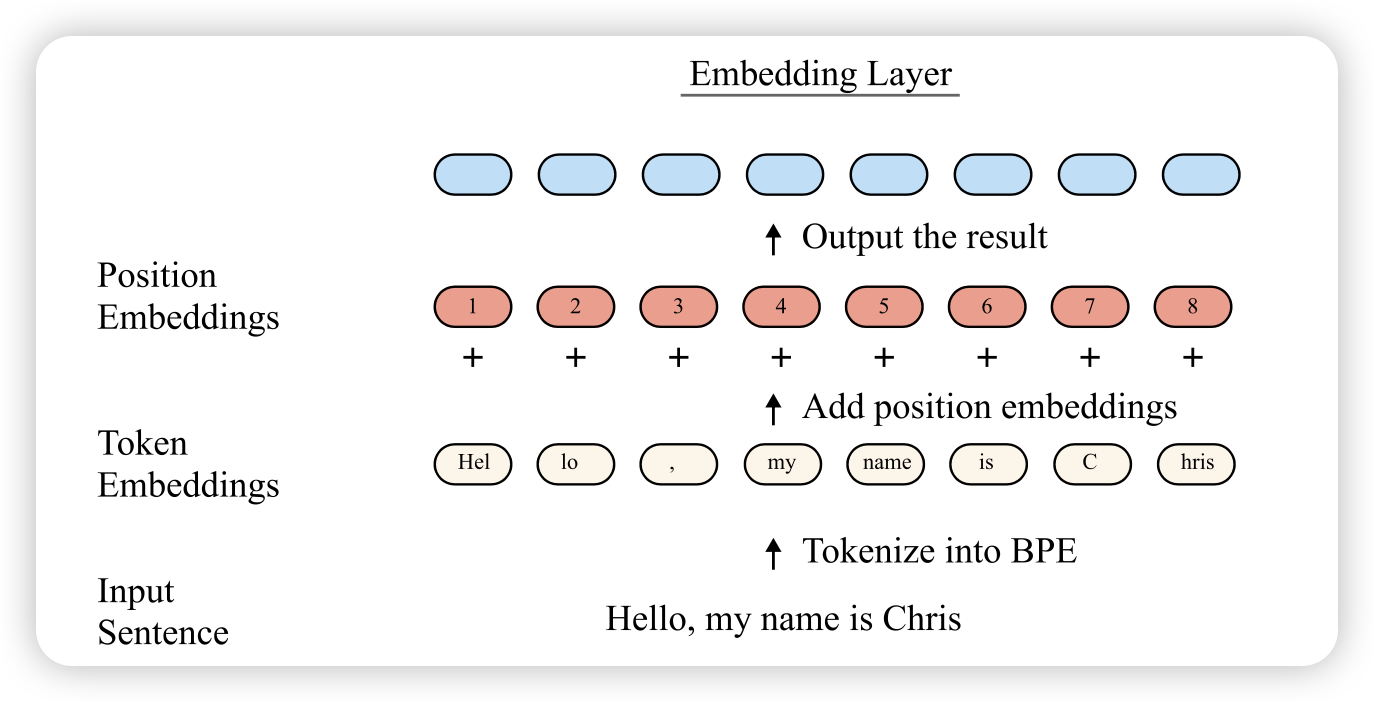
GPT-2는 입력 문장을 먼저 토큰화(tokenization)한 다음, 각 토큰을 고유한 정수 ID로 변환 함
이후 이 ID들은 nn.Embedding 레이어를 통해 고차원 벡터로 매핑. 해당 벡터는 학습 가능한 파라미터로, 의미적으로 비슷한 단어들이 비슷한 벡터값을 가지도록 학습
이 임베딩 벡터는 단어 자체만을 나타냄. 문장 내 위치 정보는 아직 포함되지 않음 → GPT-2는 포지션 임베딩(position embedding)도 함께 반영. 이 포지션 임베딩도 학습 가능한 벡터고, 토큰이 문장 내 몇 번째에 위치하는지를 나타냄
최종적으로 모델에 들어가는 임베딩은 다음 두 가지를 더한 것
- 토큰 임베딩 (단어의 의미)
- 포지션 임베딩 (단어의 위치)
이렇게 만들어진 임베딩은 이후 transformer layer의 input으로 들어감
context lenght
GPT-2 모델 기준으로는 임베딩 차원은 768이고, 최대 1024개의 토큰 길이까지 지원. 한 문장이 1024개 토큰을 넘으면 자르고 넣어야 함
Tokenization
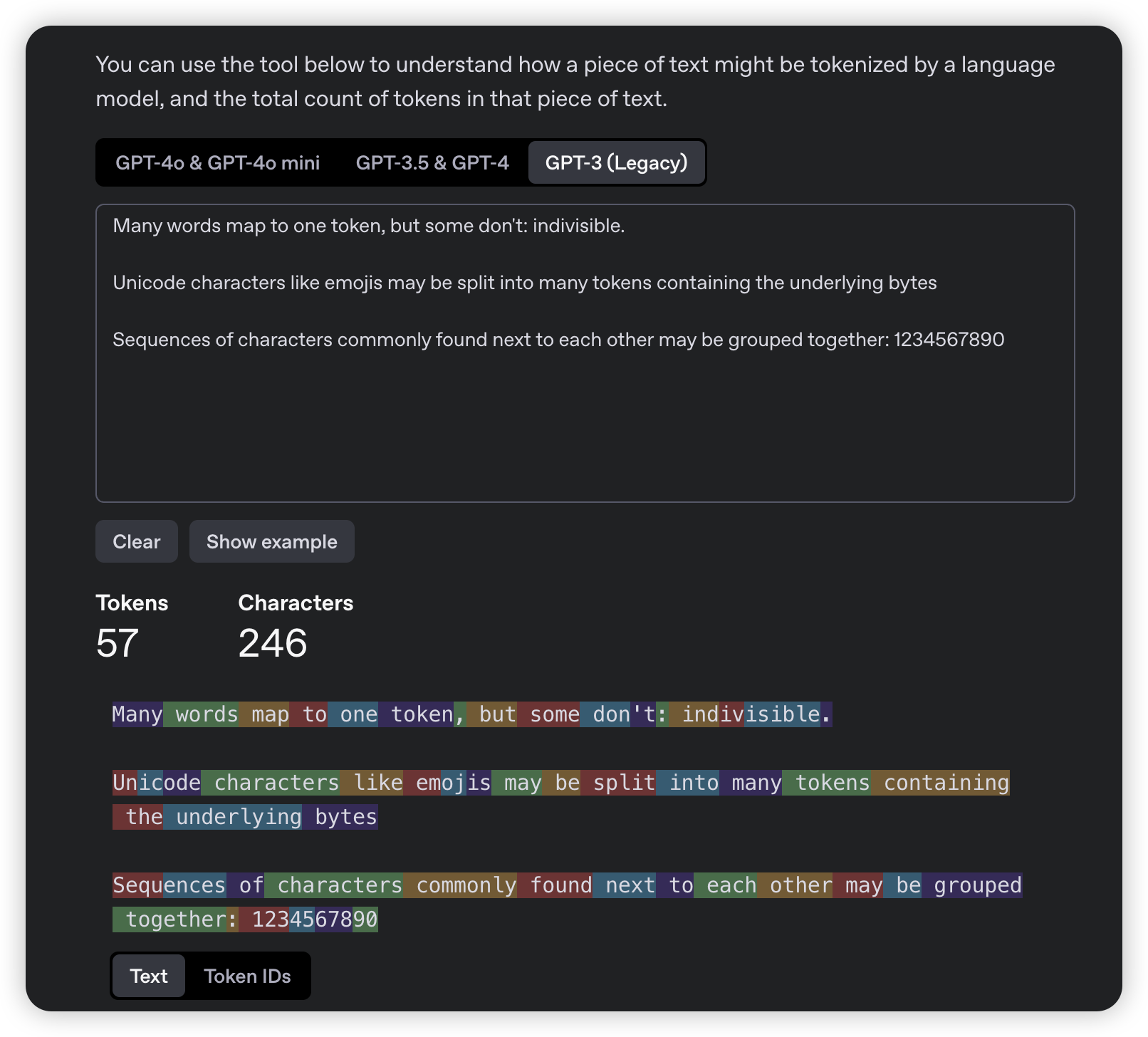
- GPT-2 model uses byte pair encoding (BPE) tokenization
 Embedding
Embedding
def embed(self, input_ids):
"""
- input_ids: [batch_size, seq_len] 형태의 토큰 ID 텐서
"""
input_shape = input_ids.size()
seq_length = input_shape[1] # 문장의 최대 길이를 구하는 용도
inputs_embeds = self.word_embedding(input_ids) # 각 토큰 ID를 임베딩 벡터로 변환
### TODO: Use pos_ids to get position embedding from self.pos_embedding into pos_embeds.
### Then, add two embeddings together; then apply dropout and return.
### YOUR CODE HERE
pos_ids = self.position_ids[:, :seq_length] # 0부터 seq_len-1까지를 잘라서 포지션에 대응하는 ID
pos_embeds = self.pos_embedding(pos_ids) # 위치 정보에 대한 임베딩 벡터값
embeds = inputs_embeds + pos_embeds # 같은 위치의 토큰 임베딩과 포지션 임베딩을 더해서 모델에 줄 최종 임베딩 벡터
embeds = self.embed_dropout(embeds) # 과적합 방지를 위해 dropout
return embeds Attention Layer
GPT-2에서는 transformer block 안에서 핵심이 되는 연산이 바로 multi-head attention
단어들 간의 관계를 파악하고, 문맥을 반영해서 표현을 강화하는 역할을 함
Multi head attention
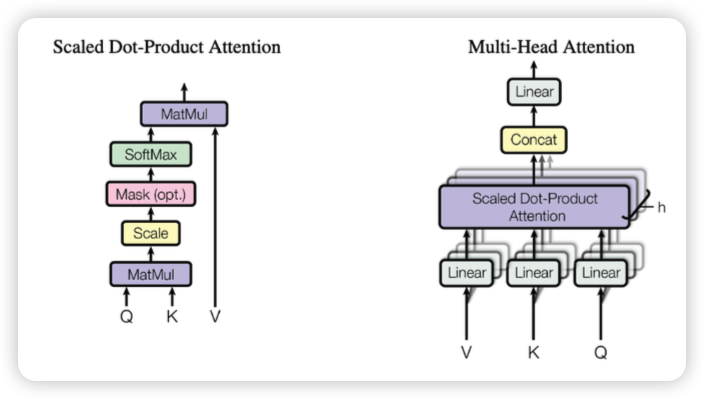 multi-head attention은 scaled dot-product attention을 여러 개 병렬로 수행하는 구조
multi-head attention은 scaled dot-product attention을 여러 개 병렬로 수행하는 구조
왼쪽 그림은 한 head에서의 attention 계산 과정을 보여주고, 오른쪽은 여러 head에서 계산한 결과를 concat하고 projection하는 전체 구조
계산 흐름은 다음과 같은 순서로 진행
- 입력 임베딩에서 Query, Key, Value를 각각 linear projection
- Q × K^T 연산 후, sqrt(d_k)로 나눠서 score 스케일링
- softmax로 attention weight 생성
- attention weight를 Value에 곱해서 weighted sum 계산
- 모든 head의 결과를 concat한 후 최종 linear layer 통과
하나의 head만 사용하는 것보다 다양한 시점에서 관계를 파악 각 head는 서로 다른 subspace에서 attention을 수행하며, 표현력을 높이는 데 도움을 줌
Causal Self Attention
GPT-2는 autoregressive 구조로 작동하기 때문에 현재 시점에서 미래 토큰을 참고하면 안 됨 이를 막기 위해 causal mask를 사용
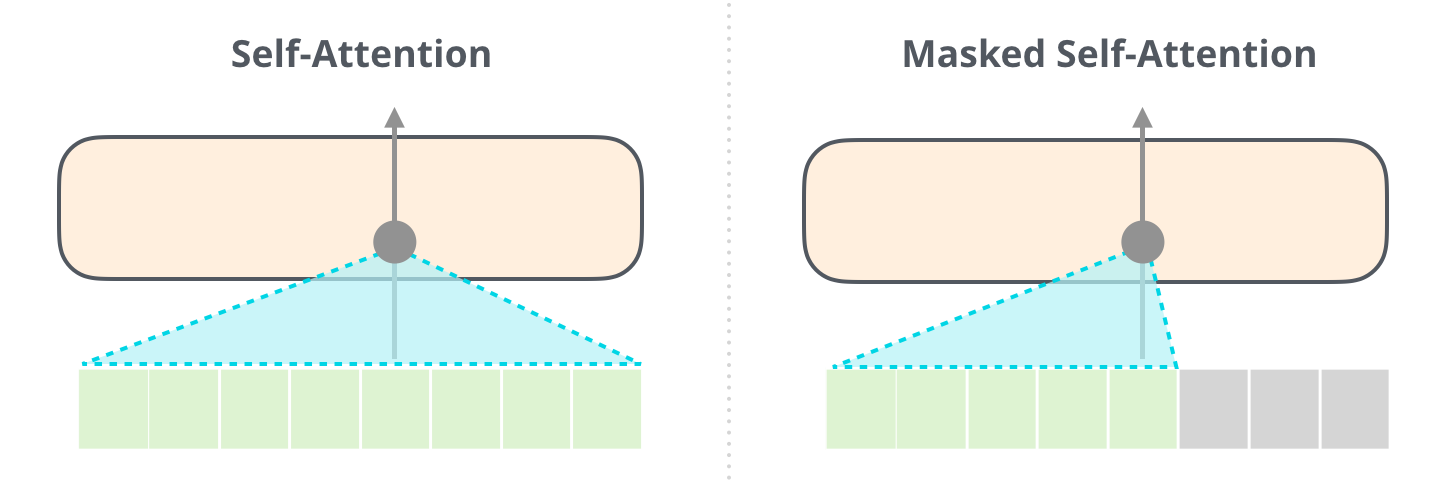
Masked Multiheaded Self-Attention
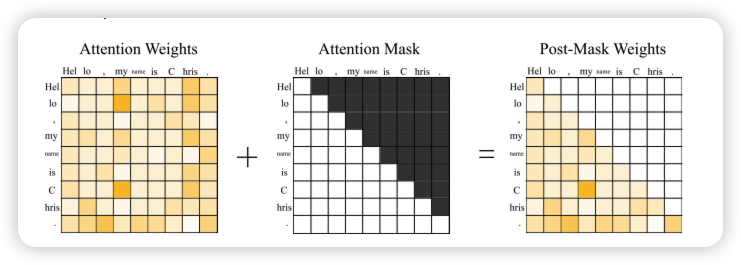
- attention score 행렬에 상삼각 마스크를 적용해 미래 토큰에 -inf 부여
- softmax 적용 시 미래에 대한 attention weight가 0이 되도록 만듦
- 결국 각 토큰은 자기 자신과 이전 토큰들만 보면서 attention을 계산함

이 과정을 masked multi-head self-attention, 또는 causal attention이라고 부름
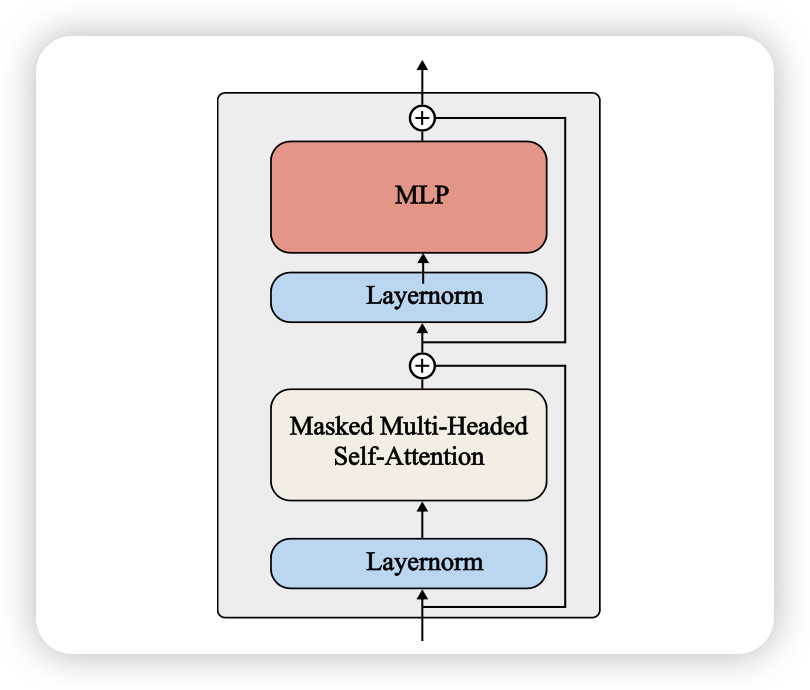
Transformer Block
GPT-2 small 모델은 총 12개의 decoder-style Transformer block으로 구성됨 각 block은 다음과 같은 구성 요소로 이루어져 있음
- Feed-Forward Network (MLP)
- LayerNorm
- Masked Multi-Head Attention
- Residual Connection (skip connection)
CausalSelfAttention 구현
def attention(self, key, query, value, attention_mask):
# Scaled dot-product attention score 계산
attn_scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-1, -2)) / (self.attention_head_size ** 0.5)
# next 토큰 참조 방지를 위한 causal mask 적용
seq_len = attn_scores.size(-1)
causal_mask = torch.triu(torch.ones((seq_len, seq_len), device=attn_scores.device), diagonal=1).bool()
attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(causal_mask, float('-inf'))
# padding token 등에 대한 attention mask 적용
attn_scores = attn_scores + attention_mask
# softmax로 attention 확률 계산 후 dropout 적용
attn_probs = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(attn_scores)
attn_probs = self.dropout(attn_probs)
# attention weight를 value에 곱해서 weighted sum 계산
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_probs, value)
attn_output = rearrange(attn_output, 'b h t d -> b t (h d)') # head 차원 다시 붙이기
return attn_output