배경
저번 세미나 리마인드 Bad logging
uvicorn이 request를 처리하는 방식(비동기) 때문에 해당 문제가 발생한게 아닌가여?
@app.get("/sync")
def sync_endpoint():
"""동기 방식으로 로그 출력"""
sync_logger.info(f"Sync log: {random.randint(0, 100)}")
return {"message": "Synchronous logging"}
@app.get("/async")
async def async_endpoint():
"""비동기 방식으로 로그 출력"""
async_logger.info(f"Async log: {random.randint(0, 100)}")
return {"message": "Asynchronous logging"}
- sync , async endpoint를 어떤식으로 처리하길래?
- 파이썬 비동기 프레임워크에서 http request를 어떻게 handling 할까?
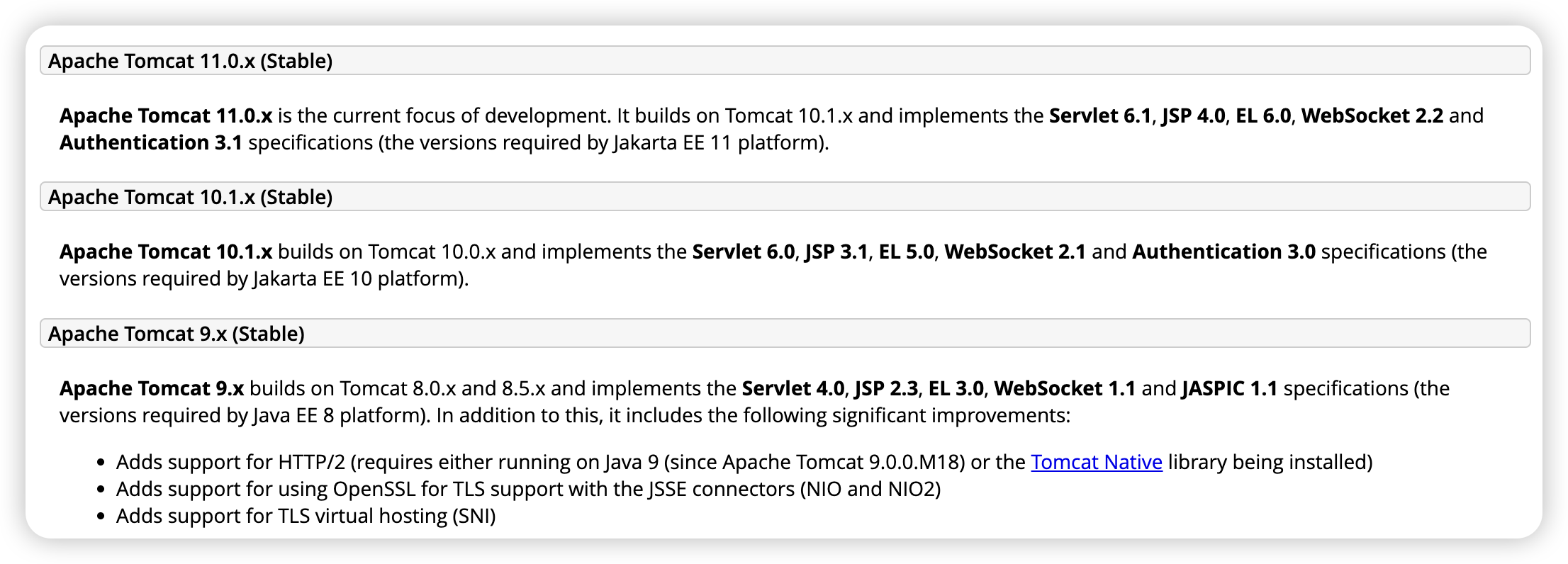
Uvicorn
starlette
ASGI server를 구현하기 위한 프레임워크
# starlette.routing
def request_response(
func: typing.Callable[[Request], typing.Awaitable[Response] | Response],
) -> ASGIApp:
"""
Takes a function or coroutine `func(request) -> response`,
and returns an ASGI application.
"""
f: typing.Callable[[Request], typing.Awaitable[Response]] = (
func if is_async_callable(func) else functools.partial(run_in_threadpool, func) # type:ignore
)
async def app(scope: Scope, receive: Receive, send: Send) -> None:
request = Request(scope, receive, send)
async def app(scope: Scope, receive: Receive, send: Send) -> None:
response = await f(request)
await response(scope, receive, send)
await wrap_app_handling_exceptions(app, request)(scope, receive, send)
return app
#
async def run_in_threadpool(func: typing.Callable[P, T], *args: P.args, **kwargs: P.kwargs) -> T:
func = functools.partial(func, *args, **kwargs)
return await anyio.to_thread.run_sync(func) # sync네?- async def가 아닌 function def는 thread connection pool에서 처리함
- 이는 일반적인 WSGI app 처리 방식과 동일
- tomcat(thread pool) or gunicorn(pre-fork)
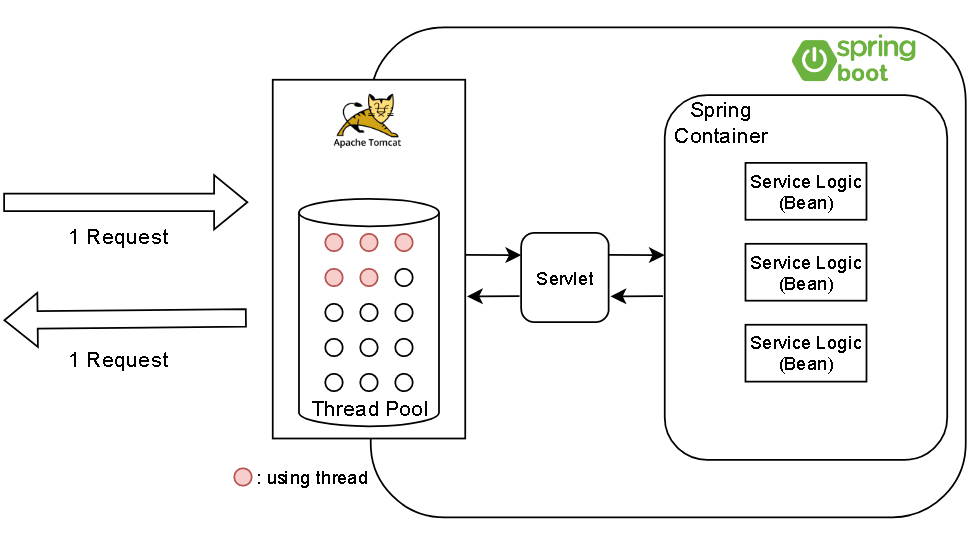
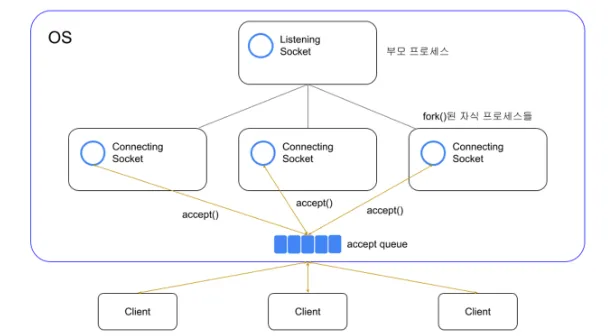
- 왜 gunicorn(python was)s thread pool을 쓰지 않고 여러 worker를 띄울까?
- GIL 때문에 결국 병렬처리에서 손해
- multi thread가 안되면, 비동기 처리로 해볼까?
uvloop
AsyncIO와 event loop을 통해 비동기 처리를 구현한 것은 동일- 다만 Python으로 구현된 AsyncIO와 달리 Cython으로 구현됌 → 성능 이점
- fs, socket IO에 대한 작업들을 이벤트 루프로 처리함
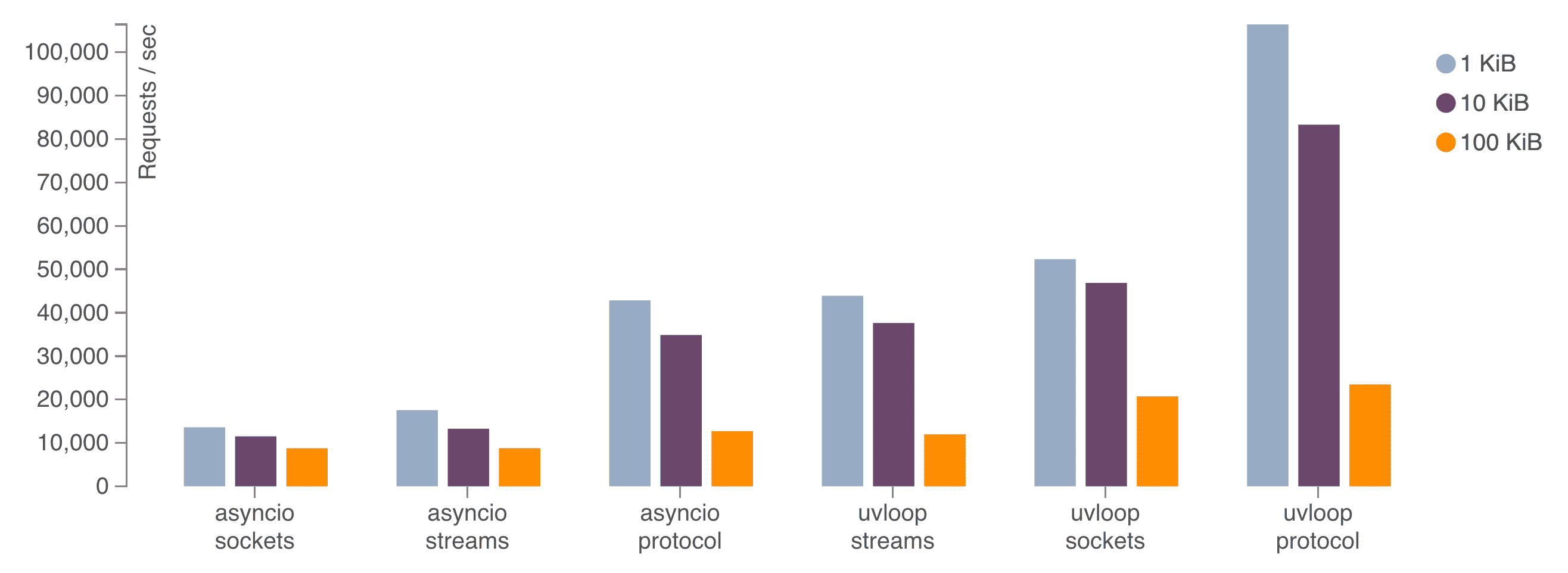
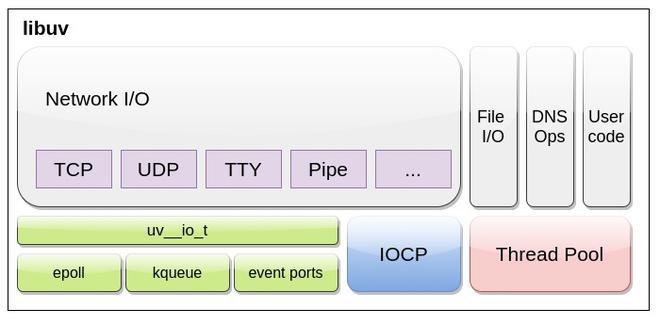
libuv
https://docs.libuv.org/en/v1.x/design.html
- Full-featured event loop backed by epoll, kqueue, IOCP, event ports.
-
file I/O 같은 경우 각 OS 별 async IO interface가 달라서 결국 동기로 처리 (multi-threading)
-
요놈이 nodejs 에서 event loop로 사용되는 c 라이브러리
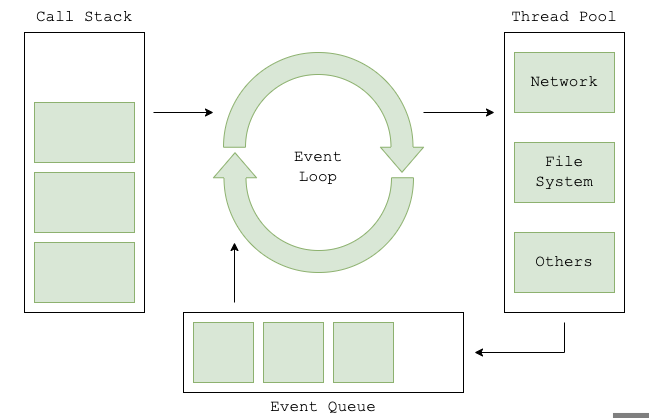
multiplexing I/O
- 비동기처리는 1 process, 1 thread에서 socket IO를 감지
epoll (kqueue, IOCP)
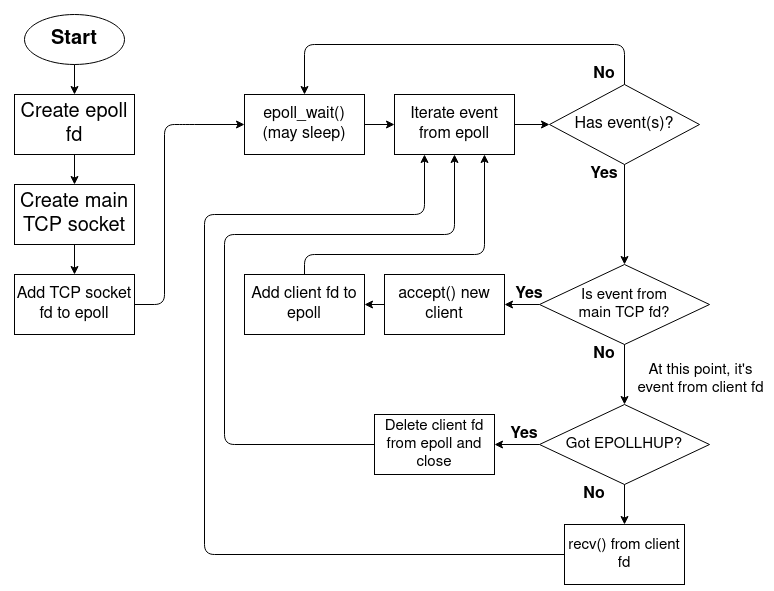
epoll server
static int event_loop(struct tcp_state *state)
{
int err;
int ret = 0;
int timeout = 3000; /* in milliseconds */
int maxevents = 32;
int epoll_ret;
int epoll_fd = state->epoll_fd;
struct epoll_event events[32];
printf("Entering event loop...\n");
while (!state->stop) {
/*
* I sleep on `epoll_wait` and the kernel will wake me up
* when event comes to my monitored file descriptors, or
* when the timeout reached.
*/
epoll_ret = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, maxevents, timeout);
if (epoll_ret == 0) {
/*
*`epoll_wait` reached its timeout
*/
printf("I don't see any event within %d milliseconds\n", timeout);
continue;
}
if (epoll_ret == -1) {
err = errno;
if (err == EINTR) {
printf("Something interrupted me!\n");
continue;
}
/* Error */
ret = -1;
printf("epoll_wait(): " PRERF, PREAR(err));
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < epoll_ret; i++) {
int fd = events[i].data.fd;
if (fd == state->tcp_fd) {
/*
* A new client is connecting to us...
*/
if (accept_new_client(fd, state) < 0) {
ret = -1;
goto out;
}
continue;
}
/*
* We have event(s) from client, let's call `recv()` to read it.
*/
handle_client_event(fd, events[i].events, state);
}
}
out:
return ret;
}
usage
- tomcat
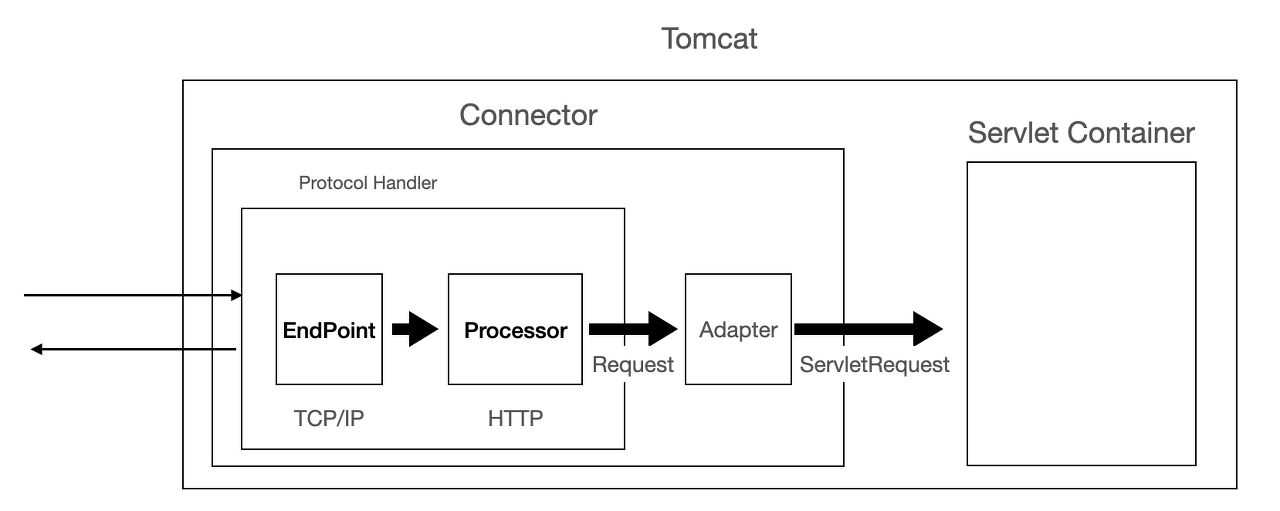
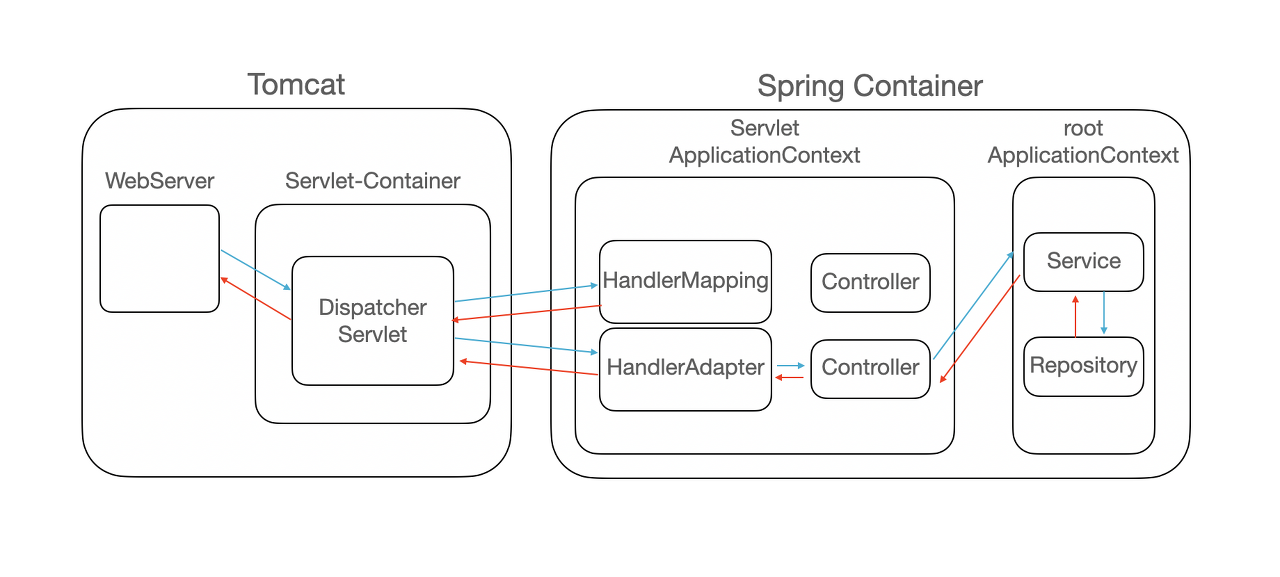
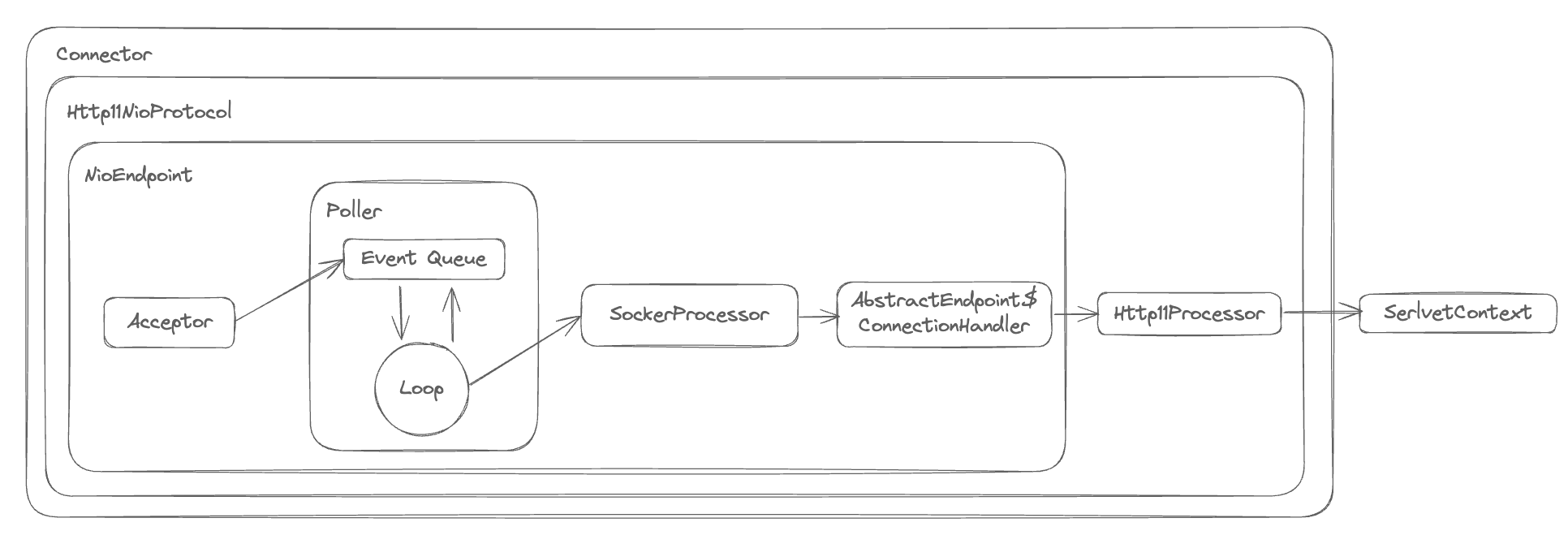
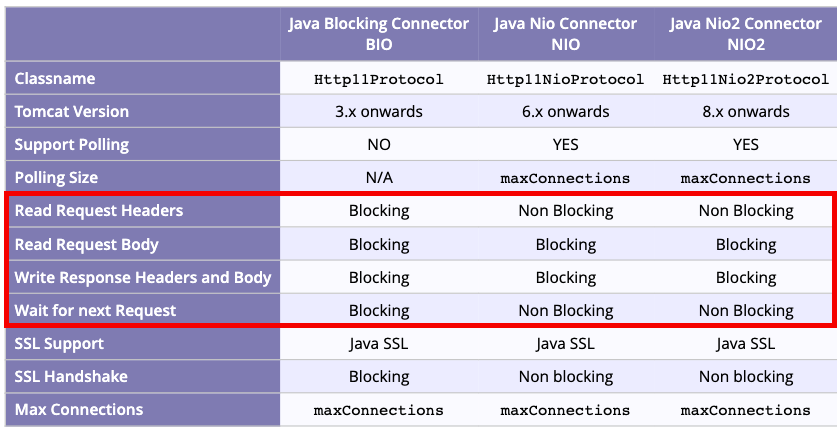
- NIO 구현체를 확인하면 epoll을 JNI로 래핑해서 사용
- NIO Selector는 플랫폼에 따라 (epoll, kqueue, IOCP)를 사용
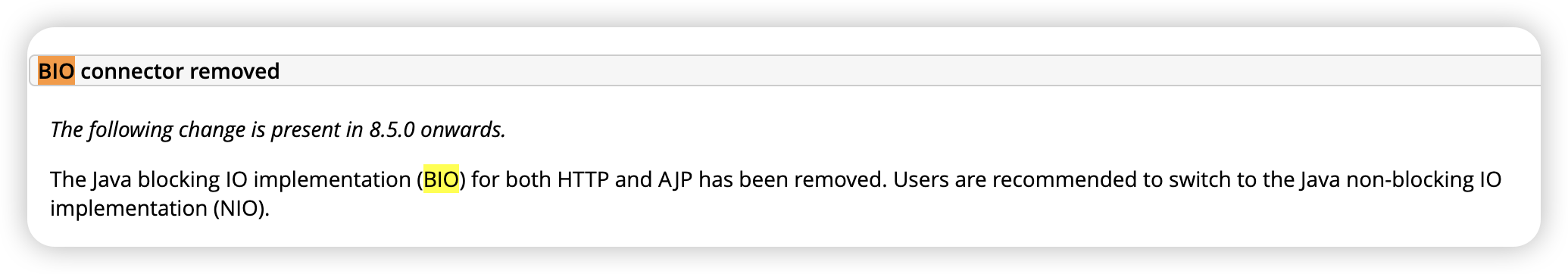
tomcat version 9부터 NIO만 지원